WHAT ARE DEEP TRADE AGREEMENTS?
Deep Trade Agreements are reciprocal agreements between countries that cover not just trade but additional policy areas, such as international flows of investment and labor, and the protection of intellectual property rights and the environment. While these agreements are still referred to as trade agreements, their goal is integration beyond trade or deep integration.
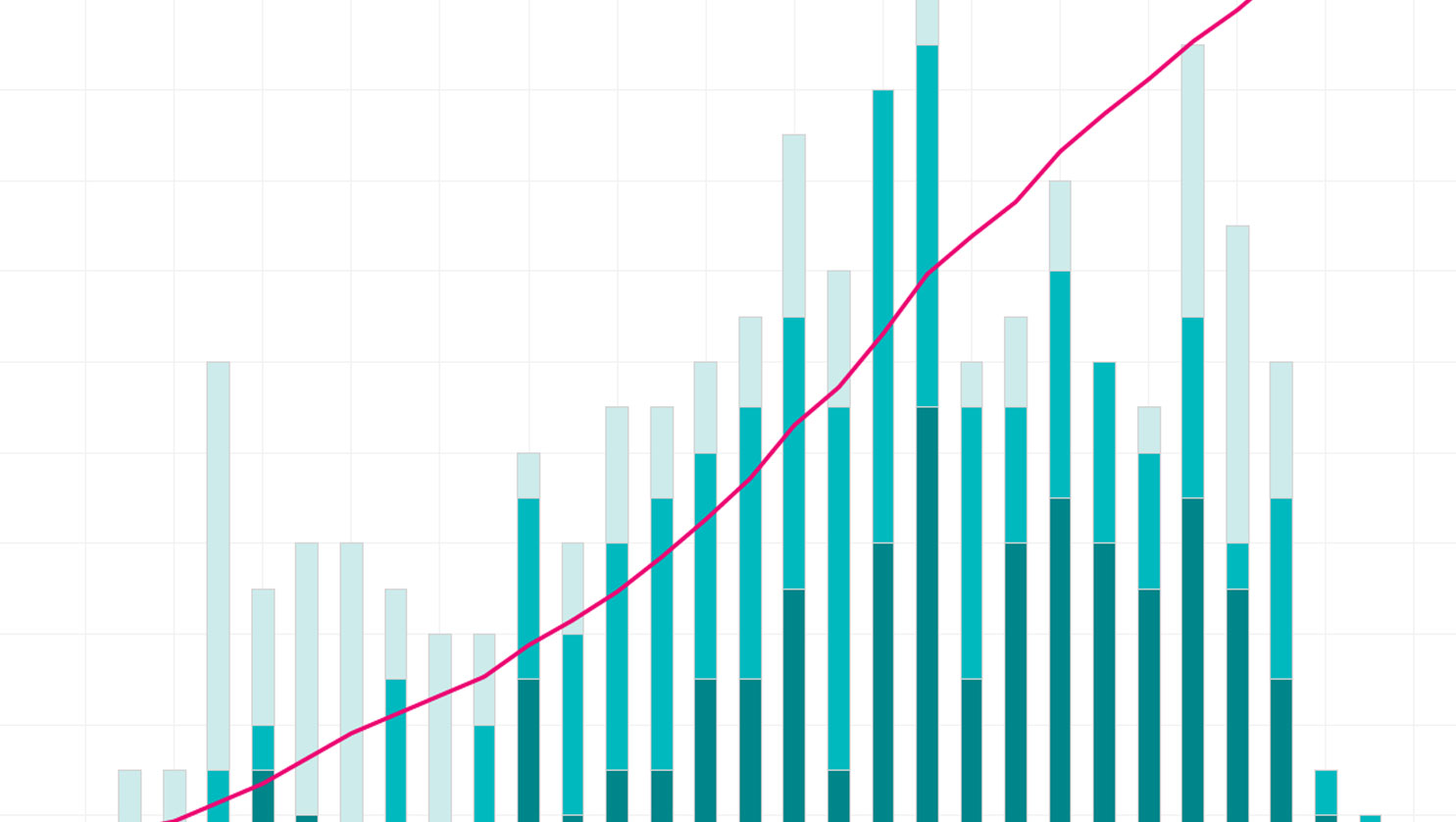
Preferential trade agreements have always been a feature of the world trading system but have become more prominent in recent years. The number of PTAs has increased from 50 in the early 1990s to more than 350 in 2023. All WTO members are currently party to at least one and often several PTAs. PTAs have expanded their scope. While the average PTA in the 1950s covered 8 policy areas, in recent years they have averaged 17.
Deep trade agreements matter for economic development. The rules embedded in DTAs, along with multilateral trade rules and other elements of international economic law such as bilateral investment agreements, influence how countries (and, hence, the people and firms that live and operate within them) transact, invest, work, and, ultimately, develop. Trade and investment regimes determine the extent of economic integration, competition rules affect economic efficiency, intellectual property rights matter for innovation, and environmental and labor rules contribute to environmental and social outcomes.
The data, research, and toolkit on deep trade agreements provided in this website will allow users to explore the new dimensions of integration across countries.